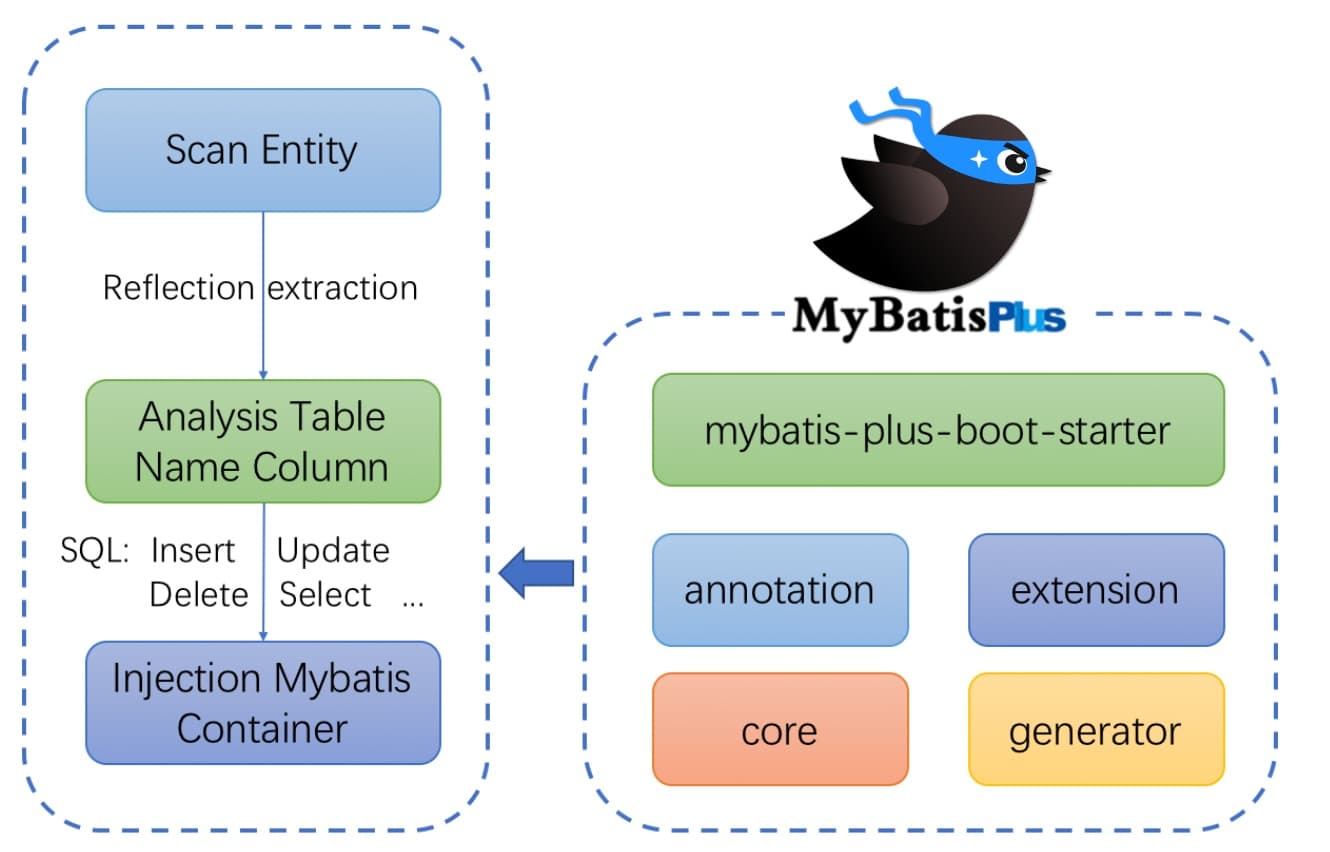
MyBatis-Plus(简称 MP)是一个 MyBatis 的增强工具,在 MyBatis 的基础上只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生。
特征
无侵入:只做增强不做改变,引入它不会对现有工程产生影响,如丝般顺滑损耗小:启动即会自动注入基本 CURD,性能基本无损耗,直接面向对象操作强大的 CRUD 操作:内置通用 Mapper、通用 Service,仅仅通过少量配置即可实现单表大部分 CRUD 操作,更有强大的条件构造器,满足各类使用需求支持 Lambda 形式调用:通过 Lambda 表达式,方便的编写各类查询条件,无需再担心字段写错支持多种数据库:支持 MySQL、MariaDB、Oracle、DB2、H2、HSQL、SQLite、Postgre、SQLServer2005、SQLServer 等多种数据库支持主键自动生成:支持多达 4 种主键策略(内含分布式唯一 ID 生成器 - Sequence),可自由配置,完美解决主键问题内置代码生成器:采用代码或者 Maven 插件可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码,支持模板引擎,更有超多自定义配置内置分页插件:基于 MyBatis 物理分页,开发者无需关心具体操作,配置好插件之后,写分页等同于普通 List 查询
就是mybatis的加强版,功能更强大
框架结构
第一个MybatisPlus工程
新建一个
sprongBoot工程在
pom文件中添加依赖1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>application.yml配置文件1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25spring:
datasource:
# 设置数据类型
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
# 驱动
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEnding=utf-8&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
username: root
password: 123456
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
# 配置日志输出
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
mapper-locations: classpath*:/mapper/**/*.xml
# 别名
type-aliases-package: com.hg.mybatisplus1.pojo
# 实体类全局配置
global-config:
db-config:
# 设置实体类对应表的统一前缀
table-prefix: t_
# 全局主键策略
id-type: assign_id数据库
sql1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user;
CREATE TABLE user
(
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
name VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
age INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
email VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
DELETE FROM user;
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email) VALUES
(1, 'Jone', 18, 'test1@baomidou.com'),
(2, 'Jack', 20, 'test2@baomidou.com'),
(3, 'Tom', 28, 'test3@baomidou.com'),
(4, 'Sandy', 21, 'test4@baomidou.com'),
(5, 'Billie', 24, 'test5@baomidou.com');实体类(使用
lombok快捷创建)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
//设置实体类所对应的表名
public class User {
/**
* TableId 将属性对应的字段指定为主键
* value : 设置数据库指定主键名
* type(enum) : 设置主键生成策略
*/
private Long id;
//指定属性中对应的字段名
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
//逻辑删除,被删除的数据查询不到,但存在
private Integer isDelete;
}创建
Mapper接口继承BaseMapper1
2
3//Repository 将类或接口标志为持久组件
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}在springBoot启动类中添加
@MapperScan扫描注解1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class MybatisPlus1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MybatisPlus1Application.class, args);
}
}测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16//lombok日志工具
public class MybatisPlusTest {
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 查询所有用户信息
*/
public void selectList(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
继承BaseMapper 实现基础的CRUD操作
插入一条数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class MybatisPlusTest {
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 插入用户
*/
public void insertUser() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("张三");
user.setAge(18);
user.setEmail("zs@136.com");
int result = userMapper.insert(user);
log.info("result:"+result);
//plus中默认使用雪花算法生成id
log.info("id:"+user.getId());
}
}删除数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public class MybatisPlusTest {
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 根据id删除用户
*/
public void deleteUserById(){
int result = userMapper.deleteById(1587839739382059009L);
}
/**
* 根据map删除用户
*/
public void deleteUserByMap(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id",2);
map.put("age",15);
int result = userMapper.deleteByMap(map);
}
/**
* 多个id批量删除
*/
public void deleteUserBatchIds(){
List<Long> list = Arrays.asList(1L, 2L, 3L);
int result = userMapper.deleteBatchIds(list);
}
}修改数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public class MybatisPlusTest {
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 根据id修改用户
*/
public void updateUser(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(4L);
user.setName("李四");
int result = userMapper.updateById(user);
log.info("result====>"+result);
}
}查询数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public class MybatisPlusTest {
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 批量查询用户
*/
public void selectUserBatchIds(){
List<Long> list = Arrays.asList(4L, 5L, 6L);
userMapper.selectBatchIds(list);
}
/**
* 根据map查询用户
*/
public void selectUserByMap(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id",4);
map.put("name","李四");
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
users.forEach((user )-> log.info("user====>"+user));
}
}使用
xml文件查询数据在
yml文件中声明扫描mapper文件
1 | mybatis-plus: |
编写mapper文件
1 |
|
实体类添加方法
1 | Map<String,Object> getUserMapById(int id); |
测试
1 |
|
通用Service接口
1 | //service接口 |
1 |
|
查询数据记录数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class ServiceTest {
private UserService userService;
public void serviceGetCount(){
long count = userService.count();
log.info("count====>"+count);
}
}批量添加数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public class ServiceTest {
private UserService userService;
/**
* 添加多个用户
*/
public void serviceBatchAddUser(){
ArrayList<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(20+i);
user.setName("user"+i);
users.add(user);
}
boolean saveBatch = userService.saveBatch(users);
log.info("saveBatch====>"+saveBatch);
}
}
常用注解
@TableName("user")设置实体类所对应的表名@TableId将属性对应的字段指定为主键,value设置数据库指定主键名type(enum): 设置主键生成策略@TableField("name")指定属性中对应的字段名@TableLogic逻辑删除,被删除的数据查询不到,但存在@Version标注版本号(乐观锁)@Repository将类或接口标志为持久组件
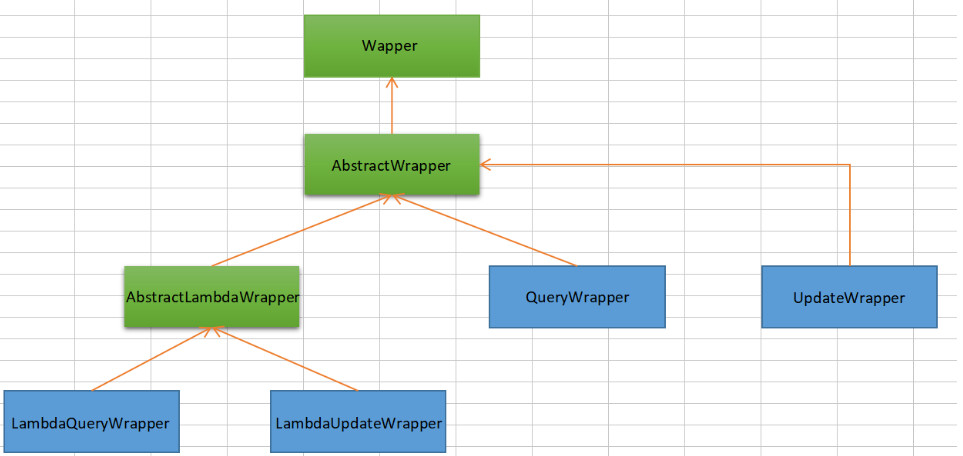
条件构造器
Wrapper: 条件构造抽象类,最顶端父类,抽象类中提供4个方法AbstractWrapper: 用于查询条件封装,生成sql的where条件AbstractLambdaWrapper:Lambda语法使用Wrapper统一处理解析lambda获取column。LambdaQueryWrapper:用于Lambda语法使用的查询WrapperLambdaUpdateWrapper:Lambda更新封装WrapperQueryWrapper:Entity对象封装操作类,不使用lambda语法UpdateWrapper: **Update条件封装,用于Entity对象更新操作
属性( 博客 )
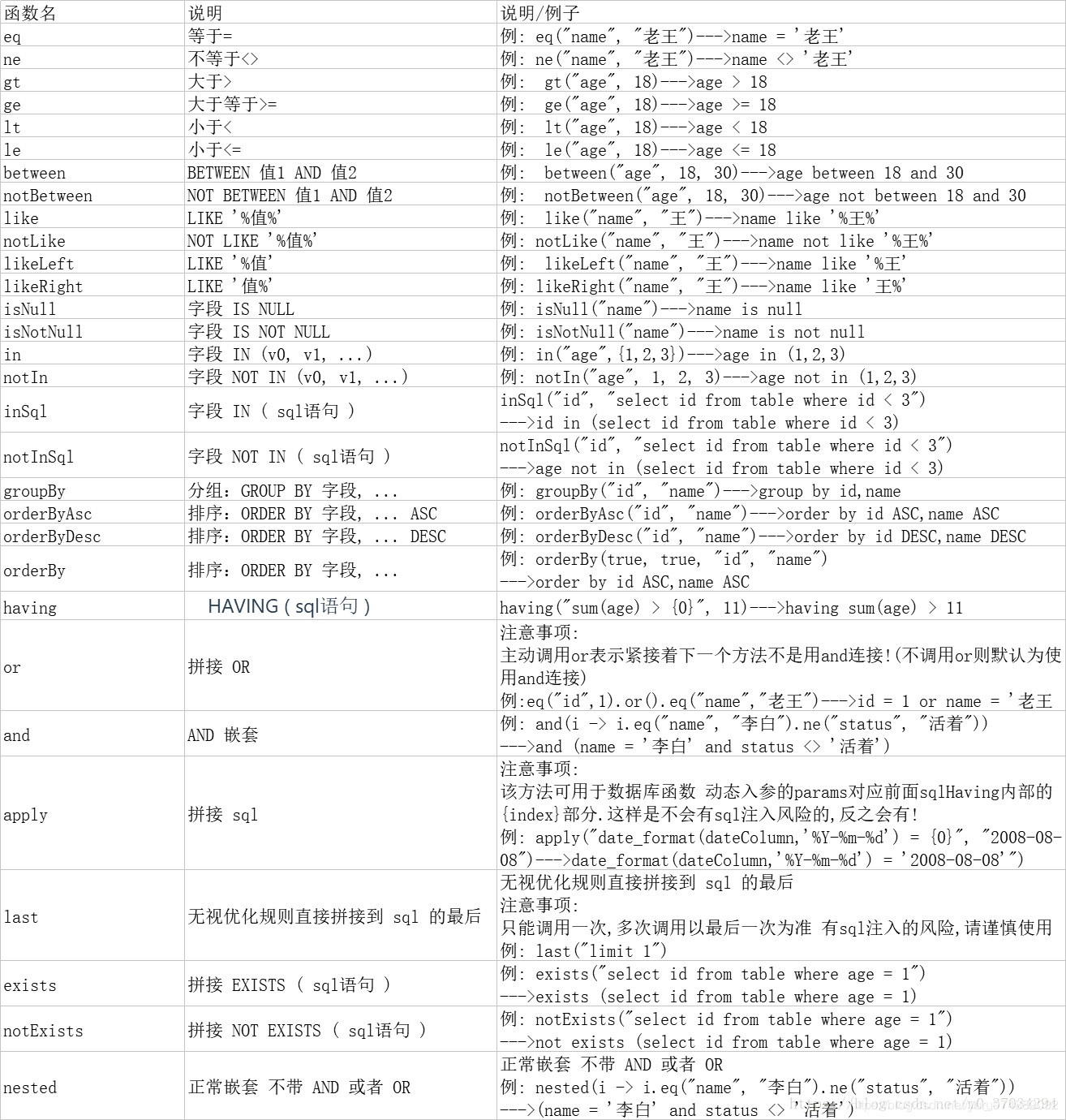
QueryWrapper构造器
1 |
|
UpdateWrapper构造器
1 |
|
Lambda语法构造器
1 |
|
MybatisPlus分页
1 |
|
自定义分页查询
接口类添加分页方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
/**
* 根据id查询用户
*/
Map<String,Object> getUserMapById(int id);
/**
* 根据年龄查询具体页面数据
* @param page mybatisPlus提供,必须放在形式参数的第一位
* @param age 年龄
* @return
*/
Page<User> selectPageVo( Page<User> page, Integer age);
}分页插件配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor(){
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
//分页插件
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL) );
return interceptor;
}
}映射文件编写sql
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
<mapper namespace="com.hg.mybatisplus1.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getUserMapById" resultType="map">
select u.id,u.name,u.age,u.email from mybatis_plus.user as u where id=#{id}
</select>
<select id="selectPageVo" resultType="user">
select * from mybatis_plus.user where age > #{age}
</select>
</mapper>测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class MybatisPlusPlugInsTest {
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 自定义分页查询
* SQL : select * from mybatis_plus.user where age > ? LIMIT ?,?
*/
public void diyPage(){
Page<User> page = new Page<>(2,3);
userMapper.selectPageVo(page,15);
page.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
乐观锁和悲观锁
乐观锁和悲观锁是两种思想,用于解决并发场景下的数据竞争问题。
乐观锁:乐观锁在操作数据时非常乐观,认为别人不会同时修改数据。因此乐观锁不会上锁,只是在执行更新的时候判断一下在此期间别人是否修改了数据:如果别人修改了数据则放弃操作,否则执行操作。
悲观锁:悲观锁在操作数据时比较悲观,认为别人会同时修改数据。因此操作数据时直接把数据锁住,直到操作完成后才会释放锁;上锁期间其他人不能修改数据。
乐观锁实现
场景
—件商品,成本价是80元,售价是100元。老板先是通知小李,说你去把商品价格增加50元。小李玩游戏,耽搁了一个小时。正好一个小时后,老板觉得商品价格增加到150元,价格太高,可能会影响销量。又通知小王,把商品价格降低30元。
此时,小李和小王同时操作商品后台系统。小李操作的时候,系统先取出商品价格100元;小王也在操作,取出的商品价格也是100元。小李将价格加了50元,并将100+50=150元存入了数据库;小王将商品减了30元,并将100-30=70元存入了数据库。因为没有锁,小李的操作完全被小王的覆盖。导致商品价格变为70元,比成本价低了10元。几分钟后,这个商品很快出售了1千多件商品,老板亏万多。
开启乐观锁插件支持
1 |
|
实体类属性添加@Version注解
1 |
|
接口
1 |
|
测试
1 |
|
悲观锁实现
悲观锁的实现,往往依靠数据库提供的锁机制
- 在对记录进行修改之前,先尝试为该记录加上排它锁
exclusive locking- 如果加锁失败,说明该记录正在被修改,那么当前查询可能要等待或者抛出异常。具体响应方式由开发者根据实际需要决定。
- 如果成功加锁,那么就可以对记录做修改,事务完成后就会解锁了
- 期间如果有其他对该记录做修改或加排它锁的操作,都会等待解锁或直接抛出异常
拿比较常用的MySql Innodb引擎举例,来说明一下在SQL中如何使用悲观锁。
要使用悲观锁,必须关闭MySQL数据库的自动提交属性,因为MySQL默认使用autocommit模式,也就是说,当执行一个更新操作后,MySQL会立刻将结果进行提交。(sql语句: set autocomment=0)
以下单过程中扣减库存的需求说明一下悲观锁的使用:
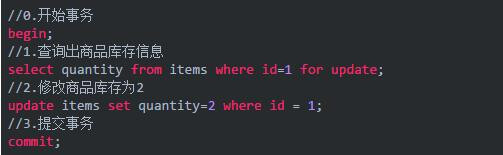
以上,在对id = 1的记录修改前,先通过for update的方式进行加锁,然后再进行修改。这是比较典型的悲观锁策略
如果以上修改库存的代码发生并发,同一时间只有一个线程可以开启事务并获得id=1的锁,其它的事务必须等本次事务提交之后才能执行。这样可以保证当前的数据不会被其它事务修改。
上面提到,使用select... for update会把数据给锁住,不过需要注意一些锁的级别,MySQL InnoDB默认行级锁。行级锁都是基于索引的,如果一条SQL语句用不到索引是不会使用行级锁的,会使用表级锁把整张表锁住
悲观锁
- 优点:悲观锁利用数据库中的锁机制来实现数据变化的顺序执行,这是最有效的办法
- 缺点:一个事务用悲观锁对数据加锁之后,其他事务将不能对加锁的数据进行除了查询以外的所有操作,如果该事务执行时间很长,那么其他事务将一直等待,那势必影响我们系统的吞吐量。
乐观锁
- 优点:乐观锁不在数据库上加锁,任何事务都可以对数据进行操作,在更新时才进行校验,这样就避免了悲观锁造成的吞吐量下降的劣势。
- 缺点:乐观锁因为是通过我们人为实现的,它仅仅适用于自己业务中,如果有外来事务插入,那么就可能发生错误。
应用场景
悲观锁:因为悲观锁会影响系统吞吐的性能,所以适合应用在写为居多的场景下。
乐观锁:因为乐观锁就是为了避免悲观锁的弊端出现的,所以适合应用在读为居多的场景下。
参考博客
知乎 [面试灵魂四问] https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/95296289
博客园 [什么是乐观锁,悲观锁] https://www.cnblogs.com/kiko2014551511/p/13129818.html
博客园 [面试题系列] https://www.cnblogs.com/kismetv/p/10787228.html
通用枚举
创建枚举
1 |
|
实体类添加枚举
1 |
|
MybatisPlus逆向工程
添加依赖
1 | <!-- mybatisPlus逆向工程代码生成器 --> |
Demo
1 | public class FastAutoGeneratorTest { |
多环境数据源
创建两个数据库,主数据库
t_product表中插入数据1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12create database `mybatis_plus_2`;
use `mybatis_plus_2`;
CREATE TABLE `t_product` (
id BIGINT(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键ID',
NAME VARCHAR(30) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品名称',
price INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '价格',
version INT(11) DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '乐观锁版本号',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
INSERT INTO t_product_1 (id, NAME, price) VALUES (1, '外星人笔记本', 100);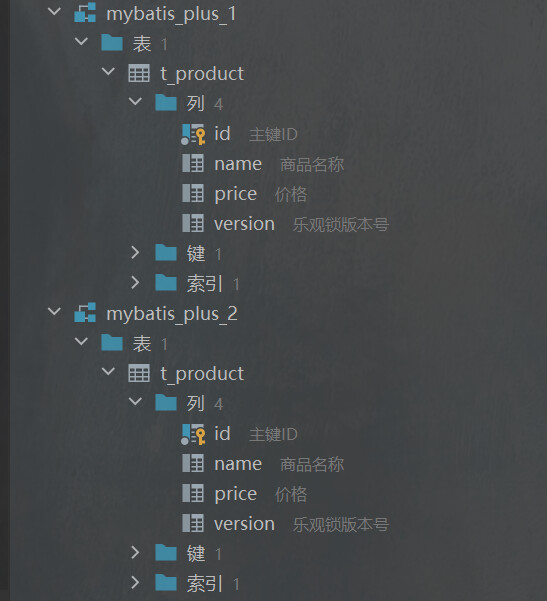
依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6<!-- 多数据源-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>dynamic-datasource-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>dynamic文档 https://www.kancloud.cn/tracy5546/dynamic-datasource/2264611配置多套数据源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28spring:
# 配置数据源信息
datasource:
dynamic:
# 设置默认的数据源或者数据源组,默认值即为master
primary: master
# 严格匹配数据源,默认false.true未匹配到指定数据源时抛异常,false使用默认数据源
strict: false
datasource:
master:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus_1?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEnding=utf-8&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
username: root
password: 123456
server_1:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus_2?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEnding=utf-8&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
username: root
password: 123456
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
#设置全局表前缀
global-config:
db-config:
# id-type: auto
table-prefix: t_
type-aliases-package: com.hg.mybatisplus.pojoService接口&实现类通过
@DS注解选择数据源1
2public interface ProductService extends IService<Product> {
}1
2
3
4//选择数据源
public class ProductServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ProductMapper, Product> implements ProductService {
}测试
主数据源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
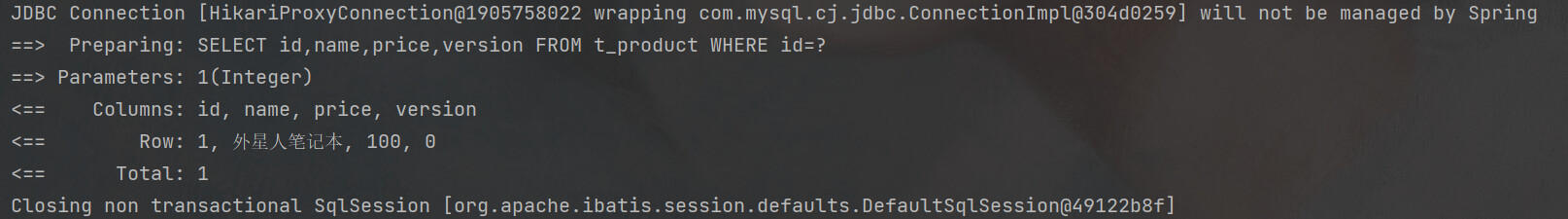
class MybatisPlus2ApplicationTests {
private ProductService productService;
void contextLoads() {
Product byId = productService.getById(1);
System.out.println(byId);
}
}
副数据源